Understanding Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) in Males
Prevention and Nutrition Strategies
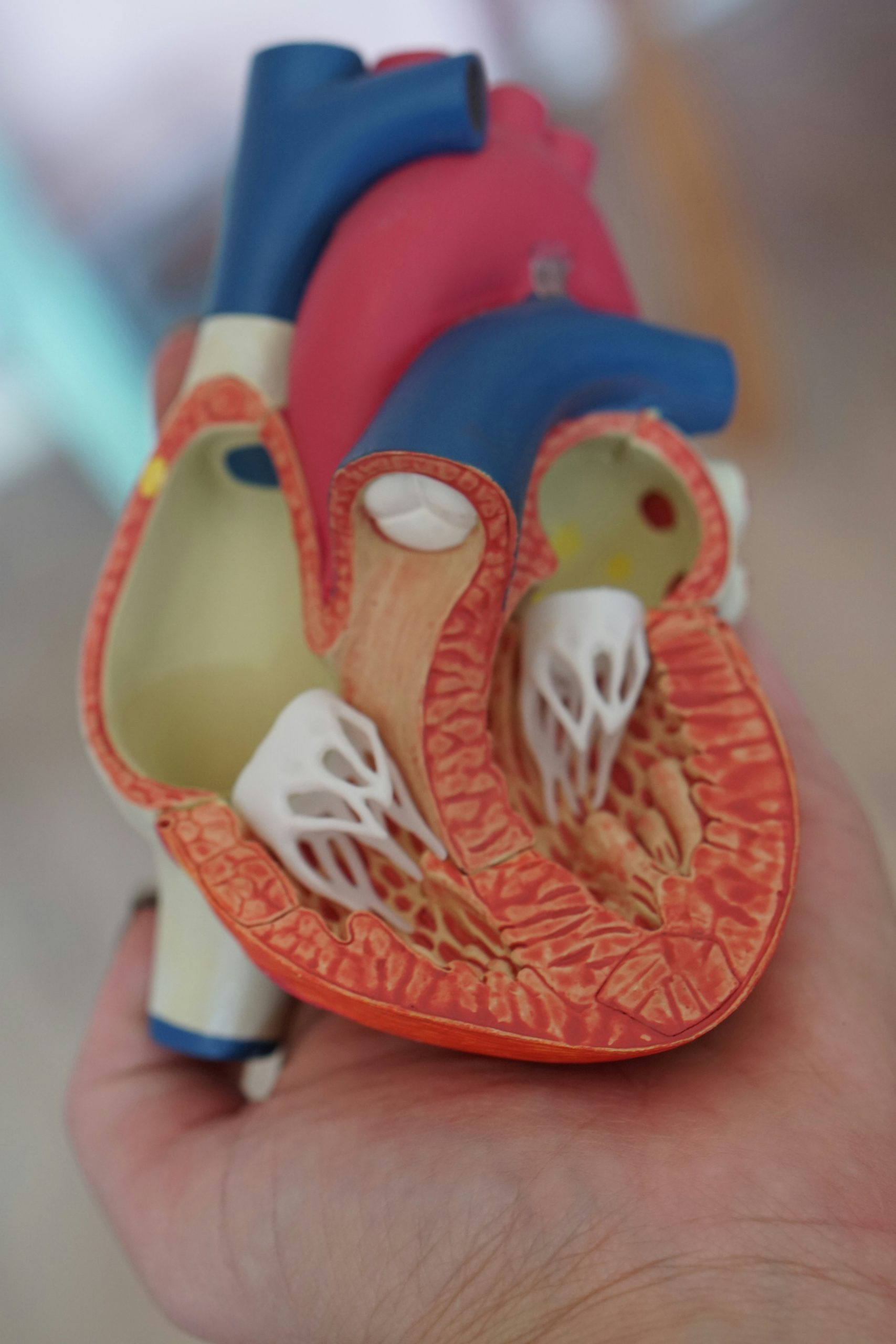
Coronary Artery Disease (CAD), also known as atherosclerosis, is a condition characterized by the gradual buildup of plaque in the coronary arteries, which supply oxygen-rich blood to the heart muscle. In males, CAD is a significant health concern, often contributing to heart attacks and other cardiovascular complications. This comprehensive guide explores the initiation of CAD, risk factors, and how nutrition plays a pivotal role in both prevention and treatment.
How CAD Starts in Males: The initiation and progression of CAD involve a complex interplay of various factors, including lifestyle, genetics, and age. The process typically begins with the accumulation of fatty deposits, cholesterol, calcium, and other substances on the inner walls of the coronary arteries. Over time, these deposits, collectively known as plaque, can narrow the arteries, restricting blood flow to the heart.
Common steps in the development of CAD include:
Endothelial Dysfunction:
- The inner lining of blood vessels, called the endothelium, may experience dysfunction due to factors like smoking, high blood pressure, or high cholesterol. This dysfunction allows for the entry of lipids and other substances into the arterial wall.
Formation of Fatty Streaks:
- Lipids, particularly low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, accumulate in the arterial wall, leading to the formation of fatty streaks.
Plaque Formation:
- Over time, inflammatory processes and the accumulation of immune cells contribute to the growth of plaques. These plaques may become unstable and prone to rupture.
Rupture and Thrombosis:
- Rupture of a vulnerable plaque can trigger the formation of blood clots (thrombosis) that can partially or completely block the coronary artery, leading to a heart attack.
Risk Factors for CAD in Males: Several risk factors increase the likelihood of developing CAD in males. While some, such as age and genetics, are non-modifiable, others are influenced by lifestyle choices. Common risk factors include:
Age and Gender:
- The risk of CAD increases with age, and males generally face a higher risk than females, particularly before menopause.
Genetics and Family History:
- A family history of CAD can contribute to an increased risk, suggesting a genetic predisposition.
High Blood Pressure:
- Hypertension puts added stress on the arterial walls, promoting the development and progression of atherosclerosis.
High Cholesterol Levels:
- Elevated levels of LDL cholesterol and low levels of high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol increase the risk of plaque formation.
Smoking:
- Tobacco smoke damages the endothelium, accelerates the progression of atherosclerosis, and contributes to plaque instability.
Diabetes:
- Diabetes, particularly poorly controlled, is a significant risk factor for CAD due to its impact on blood vessels.
Obesity and Inactivity:
- Being overweight or obese and leading a sedentary lifestyle are associated with an increased risk of CAD.
Unhealthy Diet:
- Diets high in saturated and trans fats, cholesterol, and excessive salt contribute to elevated blood lipids and hypertension.
Nutritional Strategies for CAD Prevention and Treatment in Males: Nutrition plays a crucial role in preventing and managing CAD. Adopting a heart-healthy diet can address multiple risk factors and support overall cardiovascular health:
Mediterranean Diet:
- Embrace a Mediterranean-style diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, seeds, and olive oil. This diet is associated with lower rates of heart disease.
Limit Saturated and Trans Fats:
- Reduce the intake of saturated fats found in red meat, full-fat dairy products, and tropical oils. Avoid trans fats commonly found in processed and fried foods.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids:
- Include sources of omega-3 fatty acids, such as fatty fish (salmon, mackerel, sardines) and flaxseeds. Omega-3s have anti-inflammatory effects and benefit heart health.
Increase Soluble Fiber:
- Foods high in soluble fiber, such as oats, beans, lentils, and fruits like apples and citrus, can help lower cholesterol levels.
Moderate Salt Intake:
- Limit sodium intake to help control blood pressure. Choose fresh, whole foods over processed and salt-laden products.
Antioxidant-Rich Foods:
- Consume foods rich in antioxidants, including fruits and vegetables, to combat oxidative stress and inflammation.
Limit Added Sugars:
- Reduce the consumption of added sugars, as excessive sugar intake has been linked to obesity and metabolic disturbances.
Stay Hydrated:
- Maintain adequate hydration, preferably with water, to support overall health.
Supplements for CAD Prevention: While obtaining nutrients from whole foods is ideal, certain supplements may be considered under the guidance of healthcare professionals:
Omega-3 Supplements:
- Fish oil supplements can provide omega-3 fatty acids, supporting heart health. However, dosage and quality should be monitored.
Plant Sterols and Stanols:
- These compounds, available in supplement form or as fortified foods, may help lower LDL cholesterol.
Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10):
- CoQ10, found in some foods and available as a supplement, may support heart health and reduce oxidative stress.
Lifestyle Modifications: In addition to dietary changes, adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle is crucial for CAD prevention:
Regular Physical Activity:
- Engage in regular aerobic exercise, such as brisk walking, jogging, or cycling, to improve cardiovascular fitness.
Maintain a Healthy Weight:
- Achieve and maintain a healthy weight through a combination of balanced nutrition and regular physical activity.
Quit Smoking:
- If applicable, seek support to quit smoking. Smoking cessation has immediate and long-term benefits for heart health.
Manage Stress:
- Practice stress-reducing techniques, such as meditation, deep breathing, or yoga, to promote overall well-being.
Regular Monitoring and Medical Guidance: Individuals at risk of CAD or those with existing heart conditions should undergo regular medical check-ups, including cholesterol and blood pressure measurements. Medical professionals can provide personalized advice, monitor risk factors, and recommend appropriate interventions.
Conclusion: CAD is a significant health concern for males, and its prevention and management require a multifaceted approach. Nutrition plays a pivotal role in addressing modifiable risk factors, supporting heart health, and reducing the progression of atherosclerosis. By adopting a heart-healthy diet, embracing lifestyle modifications, and seeking professional guidance, individuals can take proactive steps towards preventing CAD and promoting cardiovascular well-being.
We hope you found the information provided by Thera-Mineral valuable and insightful. At Thera-Mineral, we are dedicated to offering high-quality supplements to support your health and well-being.
If you have any further questions, need additional information, or would like to explore our range of supplements, please don’t hesitate to reach out. You can contact us at our office located at 25216 Grogan’s Park Dr. Suite A, The Woodlands, TX 77380. Our friendly team is ready to assist you by phone at 855-472-2569 or via email at support@theramineral.com.
For your convenience, most supplements are available on our website, theramineral.com. However, if you don’t find a specific product on the site, our dedicated staff can help you place an order, and we’ll ensure it’s delivered to your place of choice.
We appreciate your trust in Thera-Mineral, and we look forward to being a reliable partner on your journey to optimal health. Thank you again for being part of our community!