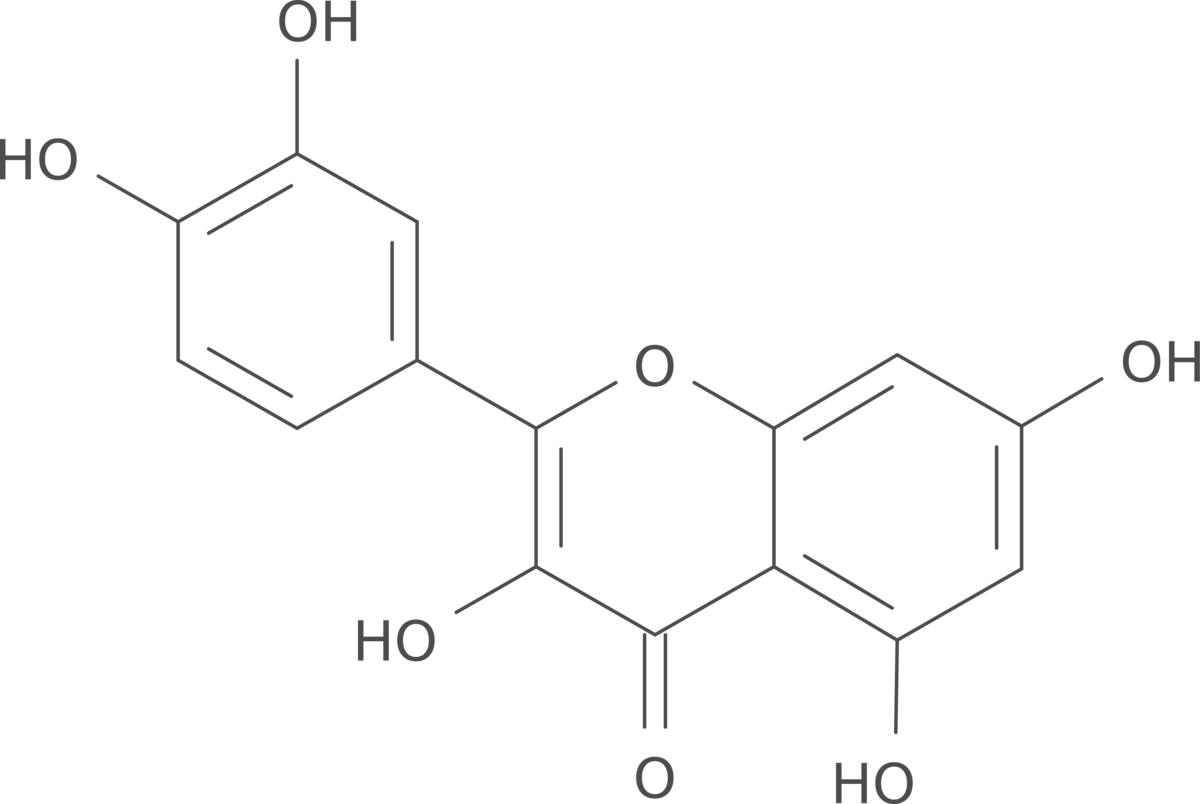
Quercetin is a flavonoid, a type of plant compound, that is widely distributed in fruits, vegetables, and herbs. It offers several potential health benefits due to its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and other biological properties. Here’s some information regarding quercetin:
Health Benefits
Quercetin has been studied for its potential effects on various aspects of human health. It may have antioxidant properties that help protect against oxidative stress and free radical damage. It also has anti-inflammatory properties that may help reduce inflammation in the body. Quercetin may support cardiovascular health, immune function, and exercise performance. Additionally, it has been investigated for its potential anticancer and neuroprotective properties, although more research is needed in these areas.
Absorption
The bioavailability of quercetin can be relatively low due to its poor solubility and limited absorption in the gastrointestinal tract. However, certain forms of quercetin, such as quercetin dihydrate or quercetin with specialized delivery systems (e.g., quercetin-phospholipid complex), may enhance its absorption and bioavailability.
Toxicity and Dosage
Quercetin is generally considered safe when consumed in normal food amounts. Toxicity studies in animals have shown no significant adverse effects even at high doses. However, the safety and toxic limits of quercetin in humans are not well-defined. It’s always recommended to follow the recommended dosage guidelines for quercetin supplements and consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice.
Long-Term Use
There is limited information on the long-term use of quercetin as a supplement. While short-term use appears to be well-tolerated, the effects of prolonged use and potential interactions with other medications or health conditions are not extensively studied. If considering long-term use, it is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional for guidance.
Sources of Quercetin
Quercetin is naturally found in a variety of plant-based foods, including apples, berries, citrus fruits, onions, leafy greens, tomatoes, and herbs such as parsley and capers. Consuming a diverse range of fruits, vegetables, and herbs can provide a good dietary source of quercetin.
Enhancing Quercetin’s Effect
Quercetin’s effects can be enhanced when combined with certain compounds, such as bromelain (an enzyme found in pineapple) or vitamin C. These combinations may improve quercetin absorption or synergistically enhance its antioxidant or anti-inflammatory properties. However, individual responses may vary, and it is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional for appropriate combinations and dosages.
Timing of Consumption
There is no specific best time of day for quercetin consumption. It can generally be taken with meals to enhance absorption, although specific product instructions should be followed.
It’s important to note that quercetin supplementation should not replace a balanced diet or medical advice. If considering quercetin supplements or higher-dose usage, it’s recommended to consult with a healthcare professional for guidance based on individual health needs and considerations.