Lutein and zeaxanthin are carotenoids that play a vital role in maintaining eye health, particularly in relation to the macula, a small area in the center of the retina responsible for sharp central vision. Here’s how lutein and zeaxanthin benefit eye health:
Macular Pigment
Lutein and zeaxanthin are naturally present in the macula, where they act as a yellow pigment known as macular pigment. This pigment helps protect the macula by absorbing harmful blue light and neutralizing free radicals, reducing the risk of oxidative damage to the cells.
Blue Light Protection
Lutein and zeaxanthin have specific filtering properties that allow them to selectively absorb blue light, a high-energy wavelength that can potentially damage retinal cells. By absorbing and filtering blue light, they help protect the retina and reduce the risk of long-term damage associated with excessive exposure to blue light.
There is no established toxic level for lutein and zeaxanthin. They are considered safe for consumption at recommended dosages. However, it’s advisable to follow the recommended daily allowances and not exceed excessively high doses without proper medical supervision.
The timing of lutein and zeaxanthin consumption is flexible and can be taken at any time of the day that suits your routine. It can be taken with or without food.
Various factors in today’s world can impact eyesight, including:
Excessive screen time
Prolonged exposure to digital screens, such as those from computers, smartphones, and tablets, can strain the eyes and contribute to digital eye strain or computer vision syndrome.
Sedentary lifestyle
Lack of physical activity and spending extended periods in a seated position can affect overall circulation and eye health.
Environmental factors
Exposure to air pollution, dust, and certain chemicals can potentially contribute to eye irritation and discomfort.
Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is one of the most common eye conditions affecting people around the world. It primarily affects the macula, leading to central vision loss and can significantly impact daily activities like reading, driving, and recognizing faces.
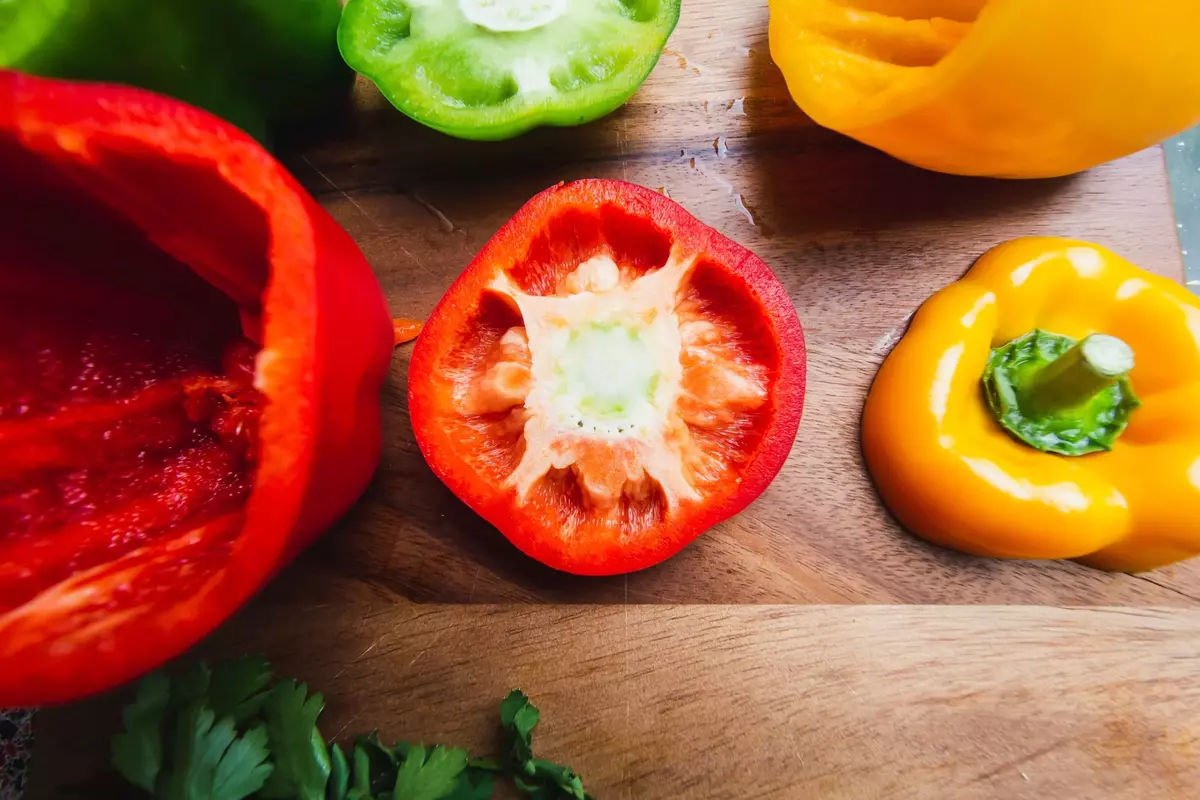 A healthy diet rich in various nutrients supports overall eye health. Foods that are beneficial for eye health include dark leafy greens (such as spinach and kale), colorful fruits and vegetables (such as carrots, bell peppers, and berries), fatty fish (such as salmon and tuna), nuts, seeds, and legumes.
A healthy diet rich in various nutrients supports overall eye health. Foods that are beneficial for eye health include dark leafy greens (such as spinach and kale), colorful fruits and vegetables (such as carrots, bell peppers, and berries), fatty fish (such as salmon and tuna), nuts, seeds, and legumes.
These foods provide essential vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and omega-3 fatty acids that support eye health.
While nutrition plays a role in maintaining overall eye health, there is no single supplement that can guarantee optimal eye health. It is generally recommended to focus on a well-balanced diet, which includes a variety of nutrient-rich foods. However, for individuals with specific eye health concerns, such as age-related macular degeneration (AMD), supplements containing a combination of antioxidants, vitamins (including lutein and zeaxanthin), and minerals may be recommended under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
Preventing eye infections through nutrition primarily involves maintaining a strong immune system, which can help protect against various infections. Consuming a well-balanced diet that includes adequate amounts of vitamins A, C, E, zinc, and selenium, along with maintaining good hygiene practices, can contribute to supporting overall immune health and potentially reduce the risk of eye infections. However, it’s important to note that proper hygiene, such as regular handwashing and avoiding contact with contaminated surfaces, is crucial in preventing eye infections.
It’s always advisable to consult with a healthcare professional or an eye care specialist for personalized advice regarding eye health, nutrition, and specific supplements based on individual needs and conditions.