Exploring Organic and Sustainable Crop Hotspots
A Global Perspective
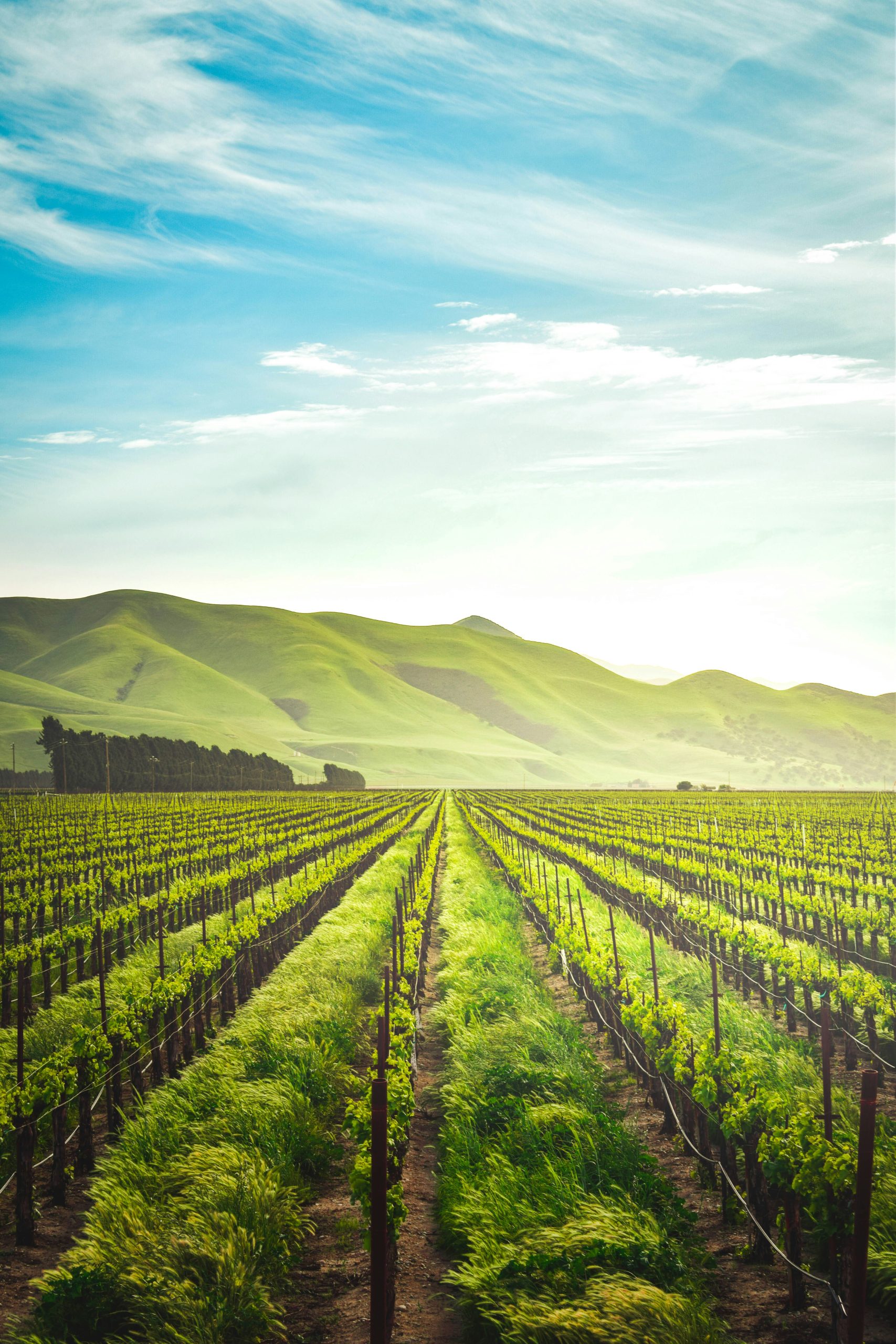
The pursuit of organic and sustainable agriculture has gained significant traction as consumers increasingly prioritize environmentally friendly and health-conscious food choices. Organic farming practices prioritize soil health, biodiversity, and eschew synthetic chemicals. Sustainable agriculture aims to minimize environmental impact, conserve resources, and promote long-term viability. As we delve into where the most organic and sustainable crops are grown worldwide, we’ll also explore the distinctions between these crops and conventionally grown ones.
Europe: Organic and Sustainable Hotspots: Europe stands out as a significant hub for organic and sustainable agriculture. Countries like Germany, France, and Italy have embraced organic farming practices, with dedicated regions known for their commitment to sustainable agriculture. The European Union has stringent regulations governing organic production, ensuring high standards and certification requirements.
Differences: Organic and sustainable crops in Europe adhere to specific principles:
No Synthetic Chemicals:
- Organic farming prohibits the use of synthetic pesticides, herbicides, and fertilizers, relying on natural alternatives.
- Sustainable agriculture emphasizes reduced dependence on chemical inputs, promoting practices like integrated pest management.
Crop Rotation and Diversity:
- Both organic and sustainable farming in Europe prioritize crop rotation and diverse planting to enhance soil fertility and reduce the risk of pests and diseases.
Conservation Practices:
- Sustainable agriculture often incorporates conservation tillage methods to minimize soil disturbance and prevent erosion.
- Organic farming promotes the use of cover crops and green manure to enrich soil structure and nutrient content.
North America: Organic and Sustainable Hotspots: In North America, regions in the United States and Canada are notable for their commitment to organic and sustainable agriculture. States like California, Vermont, and Oregon lead the way in organic crop production. The organic sector in North America has witnessed substantial growth, driven by consumer demand for pesticide-free and environmentally friendly produce.
Differences: Organic and sustainable farming practices in North America showcase distinctive features:
Certification Standards:
- Both the United States and Canada have stringent organic certification standards, ensuring compliance with organic principles.
- Sustainable farming initiatives may include programs like the Conservation Stewardship Program (CSP) in the United States, promoting environmentally beneficial practices.
Local and Community Focus:
- Sustainable agriculture in North America often emphasizes local and community-supported agriculture (CSA), fostering direct connections between farmers and consumers.
- Organic farming practices prioritize biodiversity, with a focus on preserving ecosystems and wildlife.
Asia: Organic and Sustainable Hotspots: Asia has witnessed a growing interest in organic and sustainable agriculture, with countries like India, Japan, and China making strides in adopting eco-friendly farming practices. These regions have seen an increasing number of organic farms and a rise in awareness about sustainable farming methods.
Differences: Organic and sustainable agriculture in Asia reflects unique characteristics:
Traditional Farming Wisdom:
- In many Asian countries, traditional and indigenous farming practices align with organic principles, emphasizing natural inputs and holistic approaches.
- Sustainable agriculture may draw from traditional rice-fish farming systems, demonstrating the integration of agriculture and aquaculture.
Agroecological Techniques:
- Organic farming in Asia often incorporates agroecological techniques, such as intercropping and agroforestry, to enhance resilience and sustainability.
- Sustainable agriculture initiatives in Asia address water conservation and efficient irrigation methods.
South America: Organic and Sustainable Hotspots: South America, particularly countries like Argentina and Brazil, has seen a rise in organic and sustainable farming practices. The Amazon rainforest region has also witnessed efforts to promote sustainable agriculture and curb deforestation.
Differences: Organic and sustainable agriculture in South America exhibits distinct characteristics:
Agroforestry Initiatives:
- Sustainable agriculture projects in South America may include agroforestry initiatives, integrating tree planting with crop cultivation to enhance biodiversity and ecosystem services.
- Organic farming practices may prioritize shade-grown crops, contributing to the preservation of natural habitats.
Certification Challenges:
- Some challenges in South America include the need for robust organic certification systems to ensure the authenticity of organic products.
- Sustainable agriculture efforts address concerns related to large-scale monoculture and aim to promote diversified and resilient farming systems.
Africa: Organic and Sustainable Hotspots: Africa, with its diverse agroecological zones, has regions where organic and sustainable agriculture initiatives are gaining momentum. Countries like Kenya and Ethiopia are witnessing increased interest in organic farming practices.
Differences: Organic and sustainable agriculture in Africa showcases specific characteristics:
Agroecological Diversity:
- Organic farming practices in Africa often align with agroecological diversity, with an emphasis on preserving traditional farming methods.
- Sustainable agriculture initiatives may include projects focused on soil conservation, water management, and community engagement.
Smallholder Farming:
- Many organic and sustainable farming initiatives in Africa involve smallholder farmers, emphasizing community-based approaches to enhance food security and livelihoods.
- Sustainable agriculture efforts address the challenges of climate change, promoting resilient farming systems.
Significant Differences Between Organic and Conventional Crops
Pesticide and Chemical Use:
- Organic crops prohibit the use of synthetic pesticides, herbicides, and fertilizers, relying on natural alternatives.
- Conventional crops may involve the use of synthetic chemicals to control pests and enhance crop yields.
Soil Health and Conservation:
- Organic farming prioritizes soil health through practices such as cover cropping, crop rotation, and reduced soil disturbance.
- Conventional farming practices may involve extensive plowing, which can contribute to soil erosion and degradation.
Biodiversity Preservation:
- Organic farming emphasizes biodiversity preservation through diverse planting and natural pest management strategies.
- Conventional farming may involve monoculture, potentially leading to the loss of biodiversity.
Synthetic Inputs:
- Organic crops do not use synthetic inputs, relying on organic fertilizers and natural pest control methods.
- Conventional crops may utilize synthetic fertilizers, pesticides, and herbicides.
Certification Standards:
- Organic crops adhere to strict certification standards, ensuring compliance with organic principles and practices.
- Conventional crops may follow standard agricultural practices without the specific criteria required for organic certification.
Conclusion:
The global landscape of organic and sustainable agriculture is dynamic, with regions worldwide contributing to the growth of eco-friendly farming practices. Europe, North America, Asia, South America, and Africa each bring unique perspectives, challenges, and successes to the table. While there are overarching principles that define organic and sustainable agriculture, the implementation varies based on local conditions, cultural practices, and the commitment of communities to environmentally conscious farming.
The significant differences between organic and conventional crops extend beyond the absence of synthetic chemicals. Organic and sustainable agriculture embodies a holistic approach that prioritizes soil health, biodiversity, and long-term ecological balance. As consumers increasingly value transparency, environmental stewardship, and health-conscious choices, the global movement towards organic and sustainable agriculture is likely to continue evolving, shaping the future of our food systems.
We hope you found the information provided by Thera-Mineral valuable and insightful. At Thera-Mineral, we are dedicated to offering high-quality supplements to support your health and well-being.
If you have any further questions, need additional information, or would like to explore our range of supplements, please don’t hesitate to reach out. You can contact us at our office located at 25216 Grogan’s Park Dr. Suite A, The Woodlands, TX 77380. Our friendly team is ready to assist you by phone at 855-472-2569 or via email at support@theramineral.com.
For your convenience, most supplements are available on our website, theramineral.com. However, if you don’t find a specific product on the site, our dedicated staff can help you place an order, and we’ll ensure it’s delivered to your place of choice.
We appreciate your trust in Thera-Mineral, and we look forward to being a reliable partner on your journey to optimal health. Thank you again for being part of our community!